Multiple Ticket and Pricing Options
Create as many different types of tickets as you need and set prices, ticket quantity limits, and much more!
acf domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /home/staging-poc/public_html/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6121blackhole-bad-bots domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /home/staging-poc/public_html/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6121debug-bar domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /home/staging-poc/public_html/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6121easy-pricing-tables domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /home/staging-poc/public_html/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6121geoip-detect domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /home/staging-poc/public_html/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6121members domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /home/staging-poc/public_html/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6121affiliate-wp domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /home/staging-poc/public_html/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6121pue-sales domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /home/staging-poc/public_html/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6121better-click-to-tweet domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /home/staging-poc/public_html/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6121pue-amazon domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /home/staging-poc/public_html/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6121pue-bbpress domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /home/staging-poc/public_html/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6121pue-stats domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /home/staging-poc/public_html/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6121wordpress-seo domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /home/staging-poc/public_html/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6121Create as many different types of tickets as you need and set prices, ticket quantity limits, and much more!

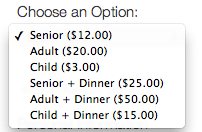 When you set multiple prices/tickets your attendees will have the option to make their own choice. You can also include tickets with options to charge for additional services or items (e.g. allowing people to register for a dinner or make a donation in addition to their registration, etc.).
When you set multiple prices/tickets your attendees will have the option to make their own choice. You can also include tickets with options to charge for additional services or items (e.g. allowing people to register for a dinner or make a donation in addition to their registration, etc.).
Checkout the WP Users (members) Addon to give your members (those logged into your website) special pricing.
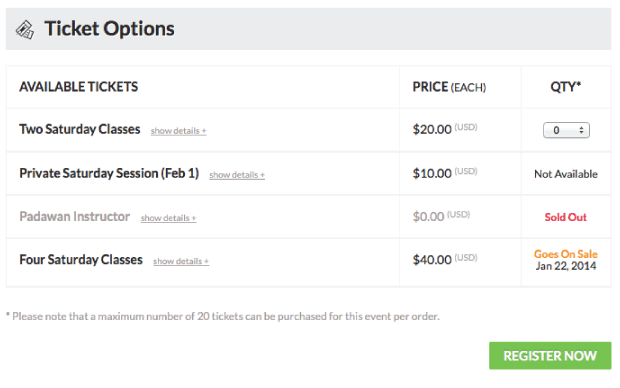
Event Espresso 4 enables event managers to create a variety of ticket options to accommodate the maximum number of attendees and collect the right fees. An unlimited number of tickets can be configured with the following options:

Event managers can control the configuration of the following options for each ticket. The ticket configuration and statuses are elegantly displayed in the front-end ticket selector on the event details page.

The names of tickets can be simple and generic e.g. “General Admission”, or specific e.g. “July 4 Ticket Only” or “Two Day VIP Pass”. This allows you to make very descriptive tickets.
Specify the exact date and time you want a ticket to become available for sale on your website. Now you can publish your event and let EE manage the rest.
Specify the exact date and time you want a ticket to become unavailable for sale on your website. As with the “Goes On Sale” setting you can publish your event and let EE manage the rest.
Indicate the starting price of the ticket (before modifier prices are applied).
Define how many of a certain type of ticket is available for sale. Once the ticket limit has been reached, that particular ticket becomes “Sold Out” (see below and the ticket selector). This helps protect you from over-selling your event.
Now is your chance to tell your attendees a great story about why they should choose a ticket. Each ticket can have a description that is displayed on the front-end in the ticket selector.
A ticket can be restricted so that it can only be used a certain number of times across available event datetimes. For example, an event may take place across 5 sessions but a ticket which has a datetime limit of 3 will permit a registrant to check-in to only 3 out of the 5 sessions.
Each ticket can have a minimum quantity of tickets that must be purchased. This allows event managers to offer bundle and tiered pricing for groups. For example, the original price of a single ticket might be $xxx.xx, but the bundle price for 5-10 tickets might be $xx.xx for each ticket. This is useful in cases where you want to sell sponsorships to your event with the requirement that the sponsors purchase more than one ticket for their company. What if you want to sell a family pack of tickets online and offer a discount for purchasing multiple tickets? Well, you can do that too. You can now configure the price of each ticket to be different based on the minimum number of tickets they have to purchase. The more tickets you require, the bigger the discount. That’s awesome!
Each ticket can have a maximum number of tickets that can be purchased. Now you can specify that someone can only purchase a single (or any other maximum you want) ticket. This feature is related to the Maximum Ticket Purchases Per Order feature because you can make it less convenient for ticket scalpers to hoard tickets or try to make more tickets available to more unique individuals.
The discount base type is a kind of Price Type that modifies the base price by subtracting a value or percentage (depending on your selected price type options). For example, a “Percent Discount” price type and “Dollar Discount” are both extensions of the “discount” base type. The “Percent Discount” price type has been set to give percentage discounts, whereas the “Dollar Discount” has been set to give specific fixed-amount dollar discounts.
Price Types based on the “surcharge” base type add to the running total. This option functions in a similar way as the discount price type described above.
Taxes are a special price type. While you can view the value of a tax price on a single ticket in the event editor, taxes are only applied to the cart total after all other modifiers have been added or subtracted from the base price.
The Event Datetimes section allows the event manager to specify which event datetimes a ticket has authorization to attend. This means that an attendee will only need one ticket to attend multiple occurrences of an event. This is useful for on-going events such as courses or classes that are non-sequential and attendees can pick and choose which dates they want to attend (from the datetimes assigned from the admin). However, when used with the # Datetimes field (see above), you can limit the number of times a ticket can be used out of the total authorized datetimes. For example an event manager can configure a ticket to allow access to all datetimes of an event (say 10 datetimes), but then set a ticket to only allow it to check-in for five of the possible datetimes. Pretty neat stuff.
The Event Espresso 4 ticket editor is intelligent and automatically controls the status of a ticket based on (one or a combination of) the event start and end datetimes, event datetime capacity limits, ticket sale start and end datetimes, and ticket availability.
There are five possible ticket statuses:
The “Active” ticket status means that a ticket is currently available for sale. A ticket is active if:
The “Upcoming” status indicates that a ticket is scheduled to become available for sale. A ticket is “Upcoming” if:
The “Sold Out” status occurs when the quantity limit of a ticket OR all assigned event datetimes quantity limits are reached. A ticket is “Sold Out” if:
The “Expired” status occurs when the “Sell Until” datetime has occurred. A ticket is “Expired” if:
The “Inactive” status occurs when the event manager has created a new ticket to replace an existing ticket. An “Inactive” ticket is automatically created when a ticket type has been sold but the event manager changes the price. This would cause data integrity issues inside Event Espresso and change registration and transaction records. The “Inactive” ticket is no longer available for sale and is replaced in the ticket selector with the new ticket.
We also make it easy to create similar tickets and delete new tickets with the “Duplicate this item” and “Trash Ticket” actions.
Each ticket that is created can also be saved as a “Default Ticket” so that it will be automatically created with any new events.